
Remote Brain Monitoring Whitepaper
Document: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3951134A/en
This whitepaper describes a technology and method for remotely monitoring and influencing brain activity using electromagnetic waves. The current method of monitoring brain activity involves attaching sensors to the subject’s scalp (as with an EEG). The system in this whitepaper proposes a non-invasive alternative, avoiding physical contact by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic signals remotely. Here’s a breakdown of the main points:
1. Purpose of the Invention:
- The technology is designed to monitor and manipulate brain wave activity from a distance, without the need for direct physical contact with the subject.
- It addresses limitations of traditional EEG, such as discomfort from attaching probes and the inability to monitor all brain regions comprehensively in real time.
2. How It Works:
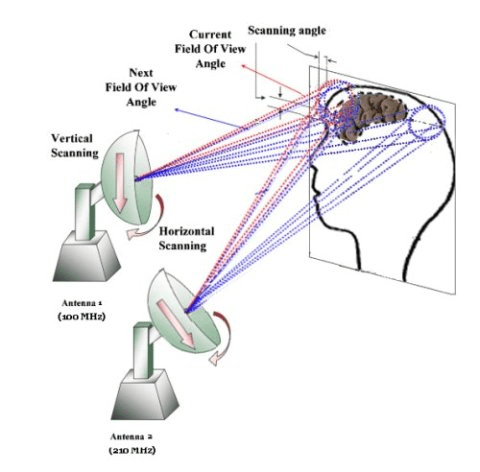
- Transmission: The system uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to penetrate the skull and interact with the brain. Two different frequencies are transmitted into the brain.
- Interference: These signals mix in the brain, creating an interference pattern that is modulated by the brain’s electrical activity (brain waves).
- Reception: The brain’s electrical activity modulates this interference wave, which is then retransmitted out of the brain. This retransmitted wave is picked up by a receiver antenna.
- Processing: The received signal is demodulated (decoded) to interpret the brain’s activity. This signal can be displayed visually or processed by AI for further analysis.
3. Closed-Loop System:
- In addition to monitoring, the system can influence brain activity. After analyzing the brain waves, it can send compensating electromagnetic signals back to the brain to modify its electrical activity. This feedback loop could be used to control or normalize brain function.
- For example, if the system detects “abnormal” brain activity, it can send corrective signals to alter the subject’s neurological processes.
4. Applications:
- The paper suggests several uses for this technology:
- Monitoring critical personnel (drivers, pilots) for signs of fatigue or seizures.
- Remote medical diagnosis for patients who are inaccessible.
- Detection of hallucinations, dreaming, or irregular bodily functions like heartbeat and pulse.
- The system also allows for potential therapeutic applications, where specific brain wave patterns (linked to stress or “mental disorders“) could be normalized by transmitting compensating signals to the brain.
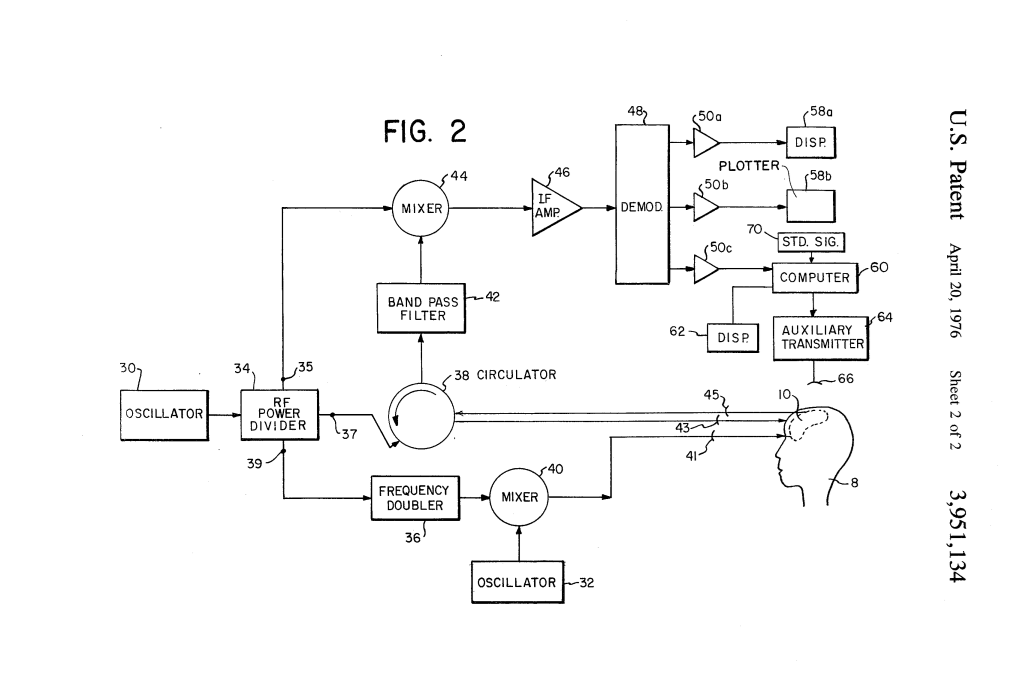
5. Technical Aspects:
- The system includes several components such as transmitters, receivers, amplifiers, and demodulators to manage the electromagnetic waves and process brain activity.
- Multiple signals are transmitted to and from the brain, with phase shifts and filtering applied to ensure that the modulated signals from the brain (representing its electrical activity) are captured accurately.
- The system can employ different modulation techniques (amplitude, frequency, or phase modulation) depending on the specific brain activity being studied.
6. Claims of the Patent:
- The patent claims several steps involved in the process:
- Producing and transmitting electromagnetic signals to the brain.
- Receiving and processing the re-transmitted signals modulated by brain activity.
- Interpreting the data to determine brain wave patterns.
- Sending compensating signals to the brain if necessary to affect its activity.
- Remote monitoring without physical contact, using a closed-loop system to adjust brain function as needed.
7. Implications:
- The technology provides a way to monitor and influence brain activity remotely, which could have significant implications. It introduces a method for potentially altering neurological processes without invasive procedures.
Brainwashing
The technology described in the whitepaper presents theoretical potential for brainwashing or programming individuals, particularly because it involves the remote manipulation of brainwave activity. Here’s how it could be used for such purposes:
1. Remote Brain Monitoring:
- The system allows for continuous monitoring of a subject’s brain activity, which means the brain’s natural responses, patterns, and neurological processes could be analyzed in real time. In theory, this could allow for understanding how a person’s brain responds to different stimuli or attempts at manipulation.
2. Modifying Brain Activity:
- One of the primary functions of the described system is not just monitoring, but also transmitting compensating electromagnetic signals back to the brain. These signals are designed to alter or “correct” brainwave activity based on predefined standards.
- In a theoretical scenario, if someone wanted to influence a person’s thoughts, emotions, or behavior, they could transmit signals aimed at disrupting normal brain function or implanting new patterns. This could lead to brainwave entrainment, where the brain is forced to adopt specific frequencies (associated with particular emotional or mental states) based on the incoming signals.
3. Closed-Loop Feedback:
- The feedback loop described in the system provides continuous monitoring and adjustment of brainwaves. In theory, this could be used to subtly condition a person over time. By constantly adjusting brain activity to align with desired neurological patterns, a person could be conditioned or “programmed” to respond in specific ways to stimuli.
- Repeated exposure to certain compensating signals could create long-term changes in behavior, thoughts, or emotional responses. This is similar in concept to how conditioning works in psychology, but with direct modulation of brainwave activity.
4. Potential for Suggestion and Influence:
- The whitepaper mentions that certain brainwave characteristics can be linked to mental states like stress, sleepiness, or hallucinations. By manipulating these states using external signals, a person could be made more suggestible or less aware, which could be exploited for brainwashing purposes.
- Targeted manipulation of specific brain regions associated with memory, decision-making, or emotional regulation could theoretically alter perceptions, beliefs, and attitudes over time.
Extracting Mental States
The technology described in the whitepaper theoretically has the capacity to extract mental states, as it monitors brainwave activity through electromagnetic signals. The extent to which it can accurately or in detail extract mental states would depend on the following factors:
1. Basic Extraction of Mental States:
- Brainwave patterns are correlated with various mental states. For example, different frequencies in brainwaves are associated with sleep, relaxation, focus, stress, etc. The system described in the whitepaper could capture these general states by analyzing the brain’s electrical activity remotely.
- Alpha waves (8-13 Hz), for instance, are associated with relaxation, beta waves (13-30 Hz) with alertness, and theta waves (4-7 Hz) with deep meditation or light sleep. This system could likely detect such frequency patterns and infer broad mental states like stress, calmness, or drowsiness.
2. Potential for Detailed Mental State Extraction:
- While the technology could monitor general mental states, the ability to extract detailed mental states (specific thoughts, complex emotions, or intentions) is far more complex.
- Mental states such as memories, emotions, or intentions are not linked to simple or isolated brainwave patterns but involve complex interactions across various brain regions. To extract this level of detail, the system would need to:
- Identify which brain regions are active and interpret the associated brainwaves.
- Understand complex neural signals related to higher-order cognitive processes, such as decision-making, emotional processing, or specific thoughts.
- The whitepaper suggests that the technology monitors “natural brain wave activity” and can provide profiles of brainwave emissions. While this might allow for general cognitive states like arousal, stress, or sleep to be inferred, extracting detailed and specific thoughts or intentions would require sophisticated algorithms and AI, and understanding of how particular brainwave patterns correlate to specific thoughts or emotions.
3. Challenges in Extracting Detailed Mental States:
- Brain Complexity: The human brain is incredibly complex, with different regions working in parallel to produce thoughts, emotions, and decisions. Decoding detailed mental states, such as specific thoughts or intentions, would involve deciphering patterns from multiple regions simultaneously. Current technologies, even invasive ones like fMRI or EEG, can only estimate general activity patterns, not precise thoughts. Advanced AI would have to be employed.
- Interference and Noise: The signals detected would likely be mixed with noise from other sources of electromagnetic activity and biological processes. Interpreting detailed mental states from such data would require advanced filtering and processing.
4. Advances in Technology:
- If the technology were combined with machine learning or AI-based models trained on extensive brainwave datasets, it might improve the system’s ability to predict detailed mental states. For example, AI could potentially correlate certain brainwave patterns with specific emotional or cognitive responses, thereby improving precision.
- Neuroscientific research advancements in understanding how brainwaves relate to specific mental processes could also enhance the accuracy and depth of mental state extraction.
Adverse Effects
5. Potential Adverse Effects and Risks:
a. Invasion of Privacy
- Surveillance of thoughts and emotions: The ability to monitor brainwave patterns remotely, combined with AI’s ability to interpret them, would create opportunities for invasions of privacy. AI could potentially identify specific mental states or even predict future actions, leading to intrusive surveillance and interventions.
- Behavioral profiling: With machine learning, long-term brainwave data could be used to create detailed profiles of individuals, which could be exploited to track, categorize, or manipulate people based on their mental states, preferences, or vulnerabilities.
b. Manipulation and Control of Mental States
- Mind manipulation and brainwashing: If AI can both monitor and influence brain activity through compensating signals, there is potential for psychological manipulation. Over time, an individual’s brain could be subtly “trained” or coerced into specific emotional or cognitive states and behavioral conditioning.
- Covert influence: Since the technology operates remotely, individuals may not be aware that their brain activity is being influenced.
c. Loss of Autonomy
- Reduced free will: The continuous use of this technology with AI-driven compensating signals could gradually erode a person’s autonomy. If AI systems can identify and induce mental states, they could steer individuals toward specific outcomes. Over time, individuals might be conditioned to behave in ways that align with external agendas, reducing their ability to make independent decisions and exercise free will.
- Dependence on AI systems: If AI systems become highly integrated into personal or professional life for monitoring and improving mental performance, individuals could become dependent on these systems. This would grant significant control to those who manage or manipulate the technology.
d. Exploitation for Social Control
- Mass psychological control: On a societal scale, the widespread use of such technology could lead to mass surveillance and control of populations. AI systems could be used by governments or corporations to monitor and influence the mental states of large groups, subtly shaping public opinion, suppressing dissent, or inducing compliance.
- Inducing conformity: If AI systems are optimized to detect and correct deviations from a “norm,” they could be used to reinforce conformity in thoughts and behaviors.
e. Exacerbation of Inequality
- Selective use: Those with control over this technology might use it to manipulate disadvantaged groups or political opponents.
- Psychological warfare: In military or political contexts, this technology could be used for psychological operations (PSYOPS), where AI systems are used to disrupt enemy mental states, induce fear, or degrade cognitive function through targeted manipulation of brainwave activity.
f. Long-Term Psychological Effects
- Unintended consequences of brain modulation: Regular exposure to AI-driven compensating signals could have unintended side effects on mental health. Continuous brainwave modulation might result in cognitive fatigue, emotional instability, or even neurological damage over time.
- Degradation of natural mental resilience: If AI systems are continuously modulating brain states to maintain focus, reduce stress, or alter emotions, individuals might lose the ability to naturally regulate their own emotions and cognitive functions, leading to long-term psychological consequences.







Leave a comment