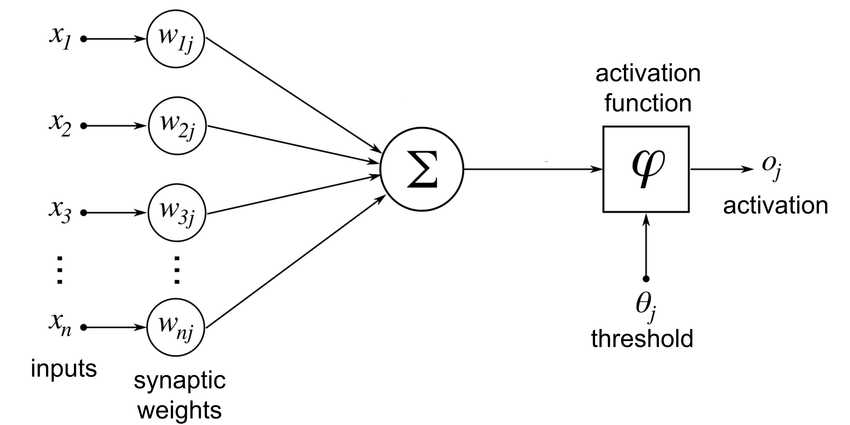
Artificial Neuron
An artificial neuron, found in computer artificial neural networks (ANN), performs a mathematical function that mimics the behavior of a biological neuron. So, can artificial neural networks become conscious?
Let’s read on to find out.
An artificial neuron works by taking several inputs, multiplying each by a specific weight (which is like adjusting the importance of that input), adding them all up, and then applying a function to decide the output. This function, called an activation function, helps the neuron decide if it should “fire” (output something) or stay silent. Think of it like a decision-making process: the neuron checks its inputs, adds them up, and then decides what to pass forward to the next layer based on a set rule.
The equation for an artificial neuron can be expressed as follows:
Weighted Sum Calculation:
The first step is to calculate the weighted sum of the input signals:

Where:
- xi are the inputs to the neuron.
- wi are the corresponding weights of the inputs.
- b is the bias term (a constant added to the weighted sum).
- z is the total weighted input to the neuron.
Activation Function:
After calculating the weighted sum, an activation function f(z) is applied to introduce non-linearity. The final output of the neuron is:

Common activation functions include:
- Sigmoid: f(z) = 1/(1+e−z1)
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): f(z) = max(0, z)
- Tanh: f(z) = tanh(z)
- Linear: f(z) = z (often used for regression tasks)
Thus, the equation of an artificial neuron combines the weighted sum and the activation function to generate the output based on its inputs and learned weights.
Biological Neuron in QR
In Quantum Realism (QR), the idea of a neuron is extended into the quantum framework, suggesting that consciousness arises from the complex interactions of quantum processes. This is especially relevant when considering how neurons operate within a biological network and how they might relate to a broader quantum network that QR proposes. Let’s explore how this applies to a biological neuron and then to consciousness within the QR framework, with hypothetical equations for each case.
A biological neuron works by receiving signals from other neurons through its dendrites, kind of like getting inputs. These signals are added up in the cell body, and if they’re strong enough, the neuron “fires” by sending an electrical signal down its axon. This signal then travels to the next neuron via synapses, where it passes on the message. It’s like a switch that turns on when enough input is received, passing the signal down the line to keep communication going in the brain.
A biological neuron operates similarly to an artificial neuron, but QR introduces the concept of quantum processing underlying the classical neural operations. QR suggests that a neuron’s behavior is not purely classical but also involves quantum effects like coherence and entanglement.
Equation for Biological Neuron in QR
In QR, the firing of a neuron (output y) could depend on both the classical weighted sum of inputs and an additional quantum term that represents quantum coherence between synapses:
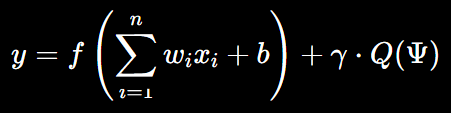
Where:
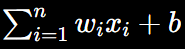 is the classical component, the weighted sum of inputs plus the bias (as in an artificial neuron).
is the classical component, the weighted sum of inputs plus the bias (as in an artificial neuron).- f(z) is the activation function (ReLU, sigmoid, or a similar biological analog).
- Q(Ψ) represents the quantum state function of the neuron, which could reflect quantum interactions like coherence, entanglement, or superposition in the synaptic network.
- γ is a scaling factor that determines the contribution of quantum effects relative to classical processes.
In QR, the equation suggests that neural behavior may involve quantum information processing, influencing how signals are transmitted through the brain’s network.
Consciousness in QR
In Quantum Realism, consciousness is hypothesized to arise from quantum processing, implying that consciousness itself could be represented as a function of quantum states within a vast network. QR suggests that consciousness is fundamental, and that it emerges from the interplay of quantum states, rather than just classical neural processes.
Hypothetical Equation for Consciousness in QR
Consciousness C can be modeled as an emergent property from the superposition and entanglement of quantum states, possibly within a network of neurons or a more abstract quantum network:

Where:
 represents the quantum superposition of states in the network, where g(ai) is a coherence function that activates specific quantum states ∣ψi⟩ within the brain or quantum field.
represents the quantum superposition of states in the network, where g(ai) is a coherence function that activates specific quantum states ∣ψi⟩ within the brain or quantum field.- Λ represents the processing bandwidth or the capacity of the quantum network (such as the brain or a broader field).
- dΛ represents the accumulation of quantum processing over time or across the network (brain).
In this equation, consciousness is seen as the integration of quantum states over the processing capacity of the network. This model aligns with the idea that consciousness is more than just the sum of neural activity but is also influenced by quantum coherence and information processing at a fundamental level.
Connecting Both Concepts
In both the biological neuron and consciousness models:
- The classical neural activity (weighted sum of inputs) plays a role.
- A quantum layer is introduced to account for deeper interactions that might influence how information is processed within the brain or how consciousness arises.
This means that while neurons in QR might function classically, the quantum effects—encoded in functions like Q(Ψ) for neurons and g(ai)∣ψi⟩ for consciousness—are crucial to understanding both the mechanics of thought and the emergence of awareness in the broader quantum framework.
Artificial Neurons Cannot Become Conscious!
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) can’t become conscious because they are purely computational systems that follow pre-programmed algorithms without any self-awareness or subjective experience. While they can process information and make decisions based on patterns in data, ANNs lack the essential qualities of consciousness, such as the ability to experience sensations, emotions, or a sense of self. Consciousness involves more than just processing inputs and outputs—it requires awareness, which isn’t something that can emerge from the mathematical operations and data manipulation that ANNs perform. Consciousness likely depends on biological processes or deeper quantum interactions, as suggested in theories like Quantum Realism, which go beyond the capabilities of current artificial systems.






Leave a comment