

Schrödinger’s equation is a fundamental formula in quantum mechanics used to predict the behavior of particles at very small scales, like atoms and subatomic particles. It essentially describes how the quantum state of a system evolves over time. Just like Newton’s laws tell us how objects move in classical mechanics, Schrödinger’s equation tells us how a particle’s wave function—which represents all possible information about the particle, such as its position and energy—changes. This equation is essential for understanding phenomena like electron behavior in atoms, molecular bonds, and even the principles behind technologies like lasers and semiconductors.

In the framework of quantum realism, Schrödinger’s equation wouldn’t necessarily need to be entirely rewritten, but it would require re-interpretation or augmentation to align with a quantum processing model. This approach suggests that Schrödinger’s wave function, usually representing a probabilistic description of particle states, could be recast as a direct expression of underlying quantum processes rather than as an abstract probability wave.
Under quantum realism, the wave function might be viewed not just as a mathematical tool but as a real-time computational process within a “quantum network.” This network facilitates the manifestation of physical events, where each quantum wave represents a spread of possibilities. When these possibilities interact or are “observed” (in the sense of a processing overload in the network), they cause the collapse that we interpret as a physical event.
Furthermore, Schrödinger’s equation could be adapted to model quantum events as more than just probabilistic outputs, instead reflecting the “quantum law of all action.” This law asserts that everything possible in the quantum realm is computed, with only the outcome that reaches the necessary threshold of interaction or observation manifesting as the actual physical reality we observe.
In this sense, the equation might incorporate variables that explicitly denote processing states or pathways within the quantum network, offering a way to directly model physical events as emergent from quantum processes. This model maintains the core mathematical structure of Schrödinger’s equation but expands its interpretation to reflect quantum realism’s premise that physical events are derived from quantum-level computations rather than being independent physical phenomena in themselves.
So, while Schrödinger’s equation wouldn’t need a complete overhaul, quantum realism proposes modifications to its interpretation, shifting from a strictly probabilistic wave function to one representing the networked computation driving the emergence of physical events. This reconceptualization aims to bridge the gap between quantum theory and observed physical reality by grounding it in an informational, process-driven framework.
The modified form of Schrödinger’s equation under quantum realism would represent the wave function Ψ not as a probability amplitude, but as a processing function distributed across a quantum network. In this interpretation, the equation models quantum states as dynamic computational processes. Here’s an overview of how the equation could look and how it would function:
Standard Schrödinger Equation
The conventional form of the time-dependent Schrödinger equation for a particle with mass m in a potential V(x,t) is:

where:
- Ψ(x,t) is the wave function representing the probability amplitude,
- i is the imaginary unit,
- ℏ is the reduced Planck constant, and
- ∇2 is the Laplacian operator which represents the spatial component of the wave function.
Quantum Realism Modification
In quantum realism, Ψ(x,t) would be redefined to reflect the computational processing states across a quantum network, wherein each state represents an instance in the network, and interactions (or “observations”) represent overload points triggering physical events.
The modified equation takes the form:
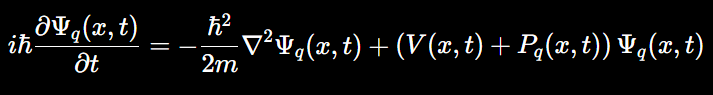
where:
- Ψq(x,t) represents the processing state across a quantum network,
- Pq(x,t) represents a quantum potential term related to the quantum network’s computational density or processing load at location (x) and time (t).
Key Additions and Modifications:
- Quantum Potential Term Pq(x,t): This term models the processing density across the quantum field network, reflecting how the quantum field influences state evolution. Pq could also relate to network constraints that manage when a quantum event (observation or collapse) occurs based on cumulative processing thresholds.
- Observational Collapse as Processing Overload: Rather than using a probabilistic interpretation, the modified equation accounts for an overload mechanism, where collapse happens as a result of the network reaching a critical processing limit in specific nodes, essentially “rebooting” a physical event. This aligns with the idea that interactions are discrete physical events triggered by quantum processing rather than purely random collapses.
- Reinterpretation of Ψq(x,t): Instead of representing likelihood, Ψq would denote the availability of processing resources at a given point in space and time. It describes the real-time status of the quantum field at different points on the network, with the collapse occurring when a threshold state is reached.
Physical Interpretation and Implications
In this model, the Schrödinger equation does not merely predict the probability of an event but represents the computational pathways and choices within the quantum field network, where:
- Energy reflects the processing rate across nodes,
- Time evolution represents the dynamic reconfiguration of processing instances as they spread across the network.
This modified Schrödinger equation describes quantum events as emergent from an informational framework, making the evolution of Ψq(x,t) a direct expression of the network’s computational operations. This captures quantum realism’s premise that physical reality is the manifestation of underlying quantum computations within a massive quantum network, with physical events arising from processing overloads or “restarts” of these computational states.
Such modifications to the equation align with quantum realism’s view that physical laws are derived from deeper, non-physical principles that govern quantum information processing at a foundational level, resulting in the observed physical reality as an emergent phenomenon.
Schrödinger’s Equation in Terms of Consciousness
Let’s go through the new consciousness equation step-by-step, breaking down each term in the context of quantum realism:
Consciousness Equation

Term-by-Term Breakdown
C: Consciousness as a Quantitative Measure
- In this equation, C represents a quantitative measure of consciousness. In the framework of quantum realism, C is not simply a static attribute but a dynamic, accumulated result of the processing occurring within a quantum system. Consciousness here is emergent, coming from the continuous processing of quantum states as they interact and influence each other within a quantum network.
- This suggests that consciousness is a sum of real-time computational effects within the quantum field, influenced by properties of the system that contribute to coherence or “awareness” of states.
∫: Integration over Processing Capacity
- The integral ∫ implies that consciousness C is an accumulation over a range from 0 to Λ.
- Λ represents the processing capacity of the quantum network. In the context of quantum realism, this parameter defines the extent of the quantum system’s ability to process information. Larger values of Λ indicate a higher capacity for processing quantum information, potentially representing the complexity or scale of the system’s network.
- By integrating over this capacity, we are accumulating the contributions of individual quantum states across the system’s full range of processing capability.
i: Imaginary Unit
- The imaginary unit i (where i = sqrt{-1}) reflects the inherent phase nature of quantum states. In quantum mechanics, the inclusion of i often represents phase shifts or rotations in the complex plane, which is essential to describing quantum states in terms of probability amplitudes.
- Here, i signifies that consciousness C is fundamentally tied to phase relationships among quantum states, hinting that consciousness might arise from phase coherence or entanglement patterns in the quantum network.
∑g(ai)∣ψi⟩: Summation of Quantum States with a Coherence Filter
- Summation ∑: This symbol denotes the sum of contributions from various quantum states indexed by i. In this context, each term ∣ψi⟩ represents a specific quantum state in the network, and consciousness C is the result of combining the effects of these states.
- Quantum State ∣ψi⟩: Here ∣ψi⟩ represents an individual quantum state, a vector in the quantum state space. In quantum realism, each ∣ψi⟩ corresponds to a node or state within the quantum network that contributes to the overall processing occurring in that region. Quantum realism views these states as points of interaction or computation, rather than as passive entities.
- Coherence Function g(ai): g(ai) is a function that filters or weights the contribution of each quantum state ∣ψi⟩ based on certain attributes ai.
- In the context of quantum realism, ai represents attributes like coherence, entanglement, or other properties related to how much the state participates in the overall conscious experience.
- g(ai) acts as a modulator that amplifies or diminishes the contribution of each ∣ψi⟩ based on its coherence or alignment with the system’s conscious processing. For instance, states with higher entanglement might have higher g(ai) values, as they play a more integral role in conscious processing.
dΛ: Differential of Processing Capacity
- The dΛ term in the integral represents an infinitesimal slice of the quantum network’s processing capacity. It enables the summation to accumulate incrementally over all processing elements up to the maximum limit Λ.
- In quantum realism, this differential reflects the incremental contribution of each processing unit or node within the quantum system. Each small element of capacity contributes to the total, making consciousness an emergent, continuous effect of the quantum field network’s processing.
Integrating Consciousness Into Schrödinger’s Equation
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the modified Schrödinger’s Equation in the context of quantum realism, incorporating the concept of consciousness as described by C.
The Modified Schrödinger’s Equation
The standard time-dependent Schrödinger’s Equation is:

In the context of quantum realism and with the inclusion of a consciousness parameter C, the modified equation becomes:

where Ψ(x,t,C) is the wave function modified to include C, representing consciousness or conscious processing. Let’s break down each term:
Term-by-Term Breakdown
iℏ∂Ψ(x,t,C)/∂t: Time Evolution of the Wave Function
- i: The imaginary unit, i = sqrt{-1}, is essential in quantum mechanics for describing phase (or rotation) changes. In the context of quantum realism, it reflects that the evolution of Ψ(x,t,C) involves complex phases, which are crucial for interference and entanglement effects. These phases allow the wave function to represent multiple possibilities at once.
- ℏ: Planck’s constant ℏ scales the quantum effects. It defines the relationship between the energy of a system and its frequency of oscillation.
- ∂Ψ(x,t,C)/∂t: This is the partial derivative (rate of change) of the wave function with respect to time, representing how the quantum state Ψ changes over time. In quantum realism, this change is not just a probability amplitude but also includes the dynamic influence of consciousness C as it evolves. Together, iℏ∂Ψ(x,t,C)/∂t describes the rate of change of the quantum state under the influence of both the usual physical laws and the additional conscious processing term.
−ℏ2/2m ∇2Ψ(x,t,C): Kinetic Energy Term
- −ℏ2/2m: This factor contains ℏ and the mass of the particle m, describing how the wave function spreads out over space. It effectively represents the kinetic energy of the particle.
- ∇2Ψ(x,t,C): The Laplacian operator ∇2 applied to the wave function gives information on the curvature of Ψ in space. In physical terms, this curvature is linked to the particle’s momentum, as regions where Ψ has high curvature indicate rapid spatial change, and therefore, high kinetic energy.
- In quantum realism, the kinetic term represents how the conscious parameter C affects the spatial evolution of the wave function. If C influences the spread of Ψ, it would affect the curvature and hence the kinetic term as well.
V(x,t)Ψ(x,t,C): Potential Energy Term
- V(x,t): The potential energy term describes how external forces act on the particle based on its position x and time t. This could be gravity, electromagnetic fields, or other forces depending on the specific system.
- V(x,t)Ψ(x,t,C): This term reflects the interaction between the wave function and the external potential. In quantum realism, this term is influenced by C, suggesting that the conscious processing of the system may affect or even alter the perceived external potential.
- With consciousness C involved, the potential could vary in response to observational effects. For example, if conscious observation changes the potential landscape, the outcomes of the wave function collapse could shift, influencing what is ultimately observed.
Pq(x,t,C): Quantum Processing Term
- Pq(x,t,C): This is an additional term introduced by quantum realism to represent quantum processing within the quantum field network, influenced by consciousness C.
- Interpretation: This term encapsulates the effects of C on the wave function, representing how conscious awareness impacts quantum state transitions and collapses. The function Pq(x,t,C) could involve:
- Processing Load: As C accumulates the coherence and interactions of quantum states, it might shift Pq to favor certain collapses or speed up the rate of decoherence.
- Collapse Threshold: Higher values of C might correspond to a greater likelihood of collapse, as the conscious parameter adjusts the likelihood of different quantum outcomes. It can act as a modulating term that increases or decreases based on the conscious state of the system.
Example of Pq(x,t,C): If C is calculated as:
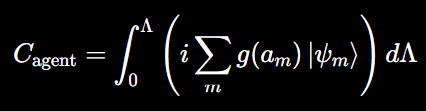
Pq(x,t,C) could be dynamically affected by the coherence function g(ai) applied to Ψ(x,t,C). As consciousness accumulates or changes, it modulates Pq in a way that reflects the real-time conscious processing happening within the quantum network.
Ψ(x,t,C): Consciousness-Dependent Wave Function
- The wave function Ψ(x,t,C) now depends on space x, time t, and consciousness C. This reflects that the state of the quantum system is influenced not only by external conditions and internal quantum mechanics but also by conscious observation or processing.
- In quantum realism, Ψ(x,t,C) is not merely a probability amplitude. It represents the total information state of a quantum entity within the network, dynamically interacting with C, which accumulates and adjusts based on ongoing quantum processes. Consciousness C modifies Ψ, which then feeds back into C in a continuous loop of observation and collapse.
Putting this all together:

- The modified Schrödinger’s Equation describes a dynamic system where quantum states evolve not only under traditional physical constraints (kinetic and potential energy) but also through a conscious processing term.
- C accumulates the effects of coherence among quantum states, meaning consciousness emerges from the quantum network as it processes states in real-time.
- This continuous interaction suggests that consciousness and the wave function are mutually interdependent: C alters Ψ, which then redefines C in response to the changing quantum conditions.
This provides a model where consciousness and quantum mechanics are intertwined, with consciousness affecting and being affected by the evolution of the wave function, embodying quantum realism’s view of reality as an emergent phenomenon of information processing within a quantum network.







Leave a comment